- Depending upon this, LC oscillators are classified as
- Hartley Oscillator
- Colpitt's Oscillator
- Hartly oscillator has in the feedback LC tank Two Inductance and On capacitance
- Colitt's oscillator has in the feedback LC tank is two capacitance and one inductance Now we understanding about Hartley oscillator
- The LC tank circuit of Hartley oscillator uses two inductance reactances and one capacitive reactance
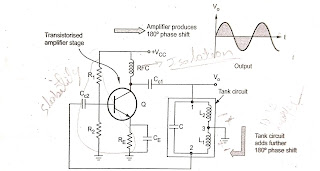
- The hartley oscillator using transistor
- The amplifier stage uses an active device as a transistor in common emittr configuration
- The resistances R1 and R2 are the biasing resistances. The RFC is the radio chocke. Its reactance value is very high frequencies, hence it can be treated as open circuit for a.c. While for d.c conditions, the reactance is zero hence causes no problem for d.c capacitors and biasing.Hence due to RFC, the isolation between a.c and .c operation is achived.
- RE is also a biasing circuit resistance and Ce is the emitter bypass capacitor. Cc1 and Cc2 are the coupling capacitors.
- the common emitter amplifier provides a phase shift of 180*. A emitter is grounded, the base and the collactor voltages are out of phase by 180*
- As the center of L1 and L2 is grounded, When upper end becomes positive, the lower becomes negative and viceversa. So they LC feedback network gives an additional shase shift of 180*. Thus the total phase shift around a loop is 360* which is necessary to satisify Barkhausen condicondition.
- To satisfy Aβ>=1, it is necessary that hfe of the transistor used in the amplifier stage must be greter then or equal to L1/L2.
- Many times instead of using two saparate inductors a single inductor wound on a core is used with grounded tapping. The part of it is used as L1 and other as L2. But in such a case they exists mutual inductance between the two gievn by M.
- The positive sign if L1 and L2 are in series aiding and negative sign if L1 and L2 are in series opposition
Hartley Oscillator
X1=X2=L and X3=C
hfe=L1/L2
where hef=Hybrid parameter forward current gain common emitter
Comments
Post a Comment